What Is An Abutment? Know Its Types & Functions
By Investoxpert | 28 Nov 2023 | Real Estate
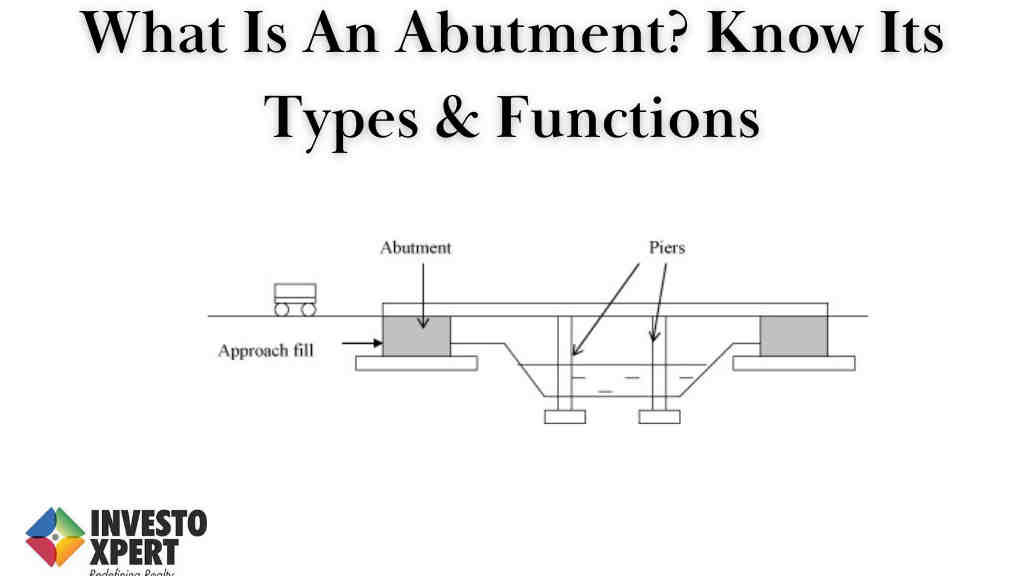
The foundation supporting the superstructure of a dam or bridge at its ends is called an abutment. Adjacents to single-span bridges function as retaining walls to prevent the earthen fill of the bridge approach from moving laterally, as well as providing vertical and lateral support for the span.
What Is An Abutment?
As the silent skeleton of a bridge, abutments are the unsung heroes of construction. Stability and load distribution are guaranteed by this flawless union of engineering and artistic expression. Let's examine this vital component that ensures the bridges can cross safely. The essay examines several abutment kinds and how they contribute to stability.
Bridges are an essential part of infrastructure, used for anything from navigating swift-moving river streams to managing traffic congestion. To guarantee stability and durability, these bridges are supported by a variety of components. Adjacents that not only close the safety gap but also lengthen the project's lifespan are one example of such an element.
Read also:- The Rise of Sustainable Living: Eco-Friendly Homes in India
Read also:- Interior Design Trends Transforming Indian Homes: Expert Insights
Read also:- ROI In Real Estate: Analysing Returns And Profits For Indian Investors
Read also:- Navigating Legalities: Essential Guidelines For Property Buyers In India
What are the functions of abutments?
- Transmission of load from a superstructure to the elements of its foundation.
- It is necessary to resist or transfer self-weight, lateral pressures (such ground pressure), and wind loads.
- To offer assistance for a single approach slab edge.
- Abutment is used to keep the vertical and horizontal force components of an arch bridge in balance.
What Is A Bridge Abutment?
An essential part of a bridge's construction, a bridge abutment acts as a support system to allow the bridge's weight be supported and transferred to the ground. In essence, abutments serve as a bridge's foundation and are essential to maintaining the stability and security of the whole construction.
Read also:- What legal points should you check while buying a property?
Read also:- Know about the Stilt Houses In Details
Read also:- Things to Explore about DDA Housing Scheme 2021
Read also:- Real Estate Trends to witness in 2021
What Are The Parts Of A Bridge Abutment?
Several essential components make up a standard bridge abutment, each of which adds to its durability and usefulness:
Foundation: Sturdily anchored to the earth to offer stability, the foundation is the base of the abutment. In order to avoid settling and guarantee the longevity of the structure, it equally distributes the load from the bridge.
Back wall: The bridge deck is supported by the vertical portion of the abutment. It offers protection against soil erosion and aids in withstanding the lateral stresses applied by the bridge.
Wing walls are slanted walls that run parallel to the ground or the embankment and connect the back wall to it. They control water movement and stop the abutment's surrounding soil from eroding.
Abutment seat- The area where the bridge deck rests on the abutment. It is essential to guarantee a stable connection between the bridge and the abutment as well as an even distribution of the weight.
What Are The Types Of Abutment In Bridge?
A variety of styles of abutments are available, each tailored to certain bridge layouts and environmental factors. The two main categories are:
Gravity abutments: To withstand the horizontal forces from the bridge, these abutments rely on their weight and the friction that exists between them and the foundation. For shorter bridges with smaller lateral strains, gravity abutments are frequently utilized.
U-shaped abutment: By spreading the bridge weight over a larger base, U-shaped abutments offer stability, much like an open-ended box does. This design resists lateral stresses by using the abutment's own weight, and it works well for shorter spans.
Cantilever wall abutment: Similar to a diving board, cantilever wall abutments have a vertical wall that extends from the foundation. Longer spans can be supported by this design, which uses the cantilevered part to counteract horizontal forces and offer stability without the need for additional support.
Full-height abutment: Full-height abutments provide robust lateral support because of their vertically extended back wall to the bridge deck. This design is frequently employed in many kinds of bridges and is efficient in withstanding both horizontal and vertical stresses, guaranteeing the stability and integrity of the entire construction.
Stub abutment: For some bridge configurations, stub abutments offer a compact and space-efficient alternative because of their shorter rear walls. Stub abutments are perfect for some design considerations, but they may need extra lateral support even for lesser spans.
Counterfort abutment: To improve the structure's resistance to lateral stresses, counterfort abutments have vertical buttresses or counterforts along the back wall. Longer spans where more reinforcing is required to preserve stability and avoid excessive deflection are best suited for this design.
Semi-stub Abutment- It lies halfway between the heights of stub abutments and full heights. Full-height abutments are built at the foot of the embankment, but others, in contrast to stub abutments, are built on or near the top.
Mechanically Stabilized Earth (MSE)-MSE stands for Mechanically Stabilized Earth. When compared to other types of abutments (piles under the bridge seat), MSE true abutments—those without piles—are less expensive. Both are substantially less expensive than concrete abutments on piles and significantly less expensive than ordinary concrete abutments.
Spill-through Abutments- Usually, these abutments are employed to support the bridge at different points throughout its length. The embankment is not maintained by wing walls or rear walls, thus the deck is supported by columns or a short wall.
What Is An Abutment In Construction?
An abutment is a part of a bridge that joins the approach roadway to the bridge and supports the superstructure of the bridge vertically at its ends.
A short bridge has one abutment built at each end that is connected to the embankment, which could have a retaining wall.
Extra abutments are erected at regular intervals throughout the length or span of longer bridges to give the support that's needed. These will provide vertical support even in the absence of a retaining wall.
Read also:- The Rise of Sustainable Living: Eco-Friendly Homes in India
Read also:- Interior Design Trends Transforming Indian Homes: Expert Insights
Read also:- ROI In Real Estate: Analysing Returns And Profits For Indian Investors
Read also:- Navigating Legalities: Essential Guidelines For Property Buyers In India
Read also:- Rental Market Trends in India: How to Make the Most of Your Investment?
Read also:- The Power of Virtual Reality in The Real Estate Business
Read also:- Mistakes to Avoid While Dealing in a Property
Read also:- Real Estate Trends That Will Rule in 2022
Read also:- RERA - All You Need To Know About Rera Gujarat Before Buying A House In 2023!
Read also:- Top 9 Amenities You Must Have In Apartments
Read also:- Why Invest In Lodha Bellagio Powai?
Read also:- Real Estate Regulations In India: RERA And Its Impact On Buyers And Developers
Read also:- Property Investment Guide For NRI’s To Invest In Indian Real Estate
Lets Get Your Dream Home
I authorize InvestoXpert and its representatives to Call, SMS, Email or WhatsApp me about its products and offers. This consent overrides any registration for DNC / NDNC.